Cambodia: Emerging Hub In Southeast Asia
Cambodia at a Glance


| GDP: | $29.5 billion (2022) |
| GDP Growth: | 5.2% (2022) 7.1% (2019) |
| Population (Urban Population %): |
16.7 million (24.7%) |
| GDP per Capita: | US$1,760 (2022) |
| Currency: | Cambodian Riel (KHR); approximately 4,055 KHR per 1 USD (April 2024) |
| Land Area: | 181,035 km2 |
| Border Countries (Border km): |
Thailand (803 km) Vietnam (1,228 km) Laos (541 km) |
| Major Cities (Population in million): |
Phnom Penh (2.3) Siem Reap (0.25) Battambang (0.12) |
Investment Highlights
01GROWING ECONOMY WITH STABLE PERFORMANCE

Cambodia's economy has not only shown consistent growth but also maintained stability amid global economic uncertainties. Despite challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the country's GDP continued to expand, reflecting its resilience. Over the past two decades, Cambodia has achieved an average annual GDP growth rate of over 6%, outpacing many of its regional peers. This sustained growth is underpinned by various factors, including robust domestic demand, increased investment inflows, and a burgeoning manufacturing sector.
Key sectors contributing to Cambodia's economic growth include manufacturing, tourism, agriculture, and construction. The manufacturing industry, particularly garment and footwear production, has experienced significant expansion, driven by favorable labor costs and preferential trade agreements with major economies. Additionally, the tourism sector, known for its cultural heritage sites and natural attractions such as Angkor Wat and coastal resorts, continues to attract millions of visitors annually, contributing significantly to GDP.
Moreover, Cambodia's agricultural sector remains a vital component of the economy, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to food security. The government's focus on agricultural modernization and diversification further enhances the sector's resilience to external shocks.
Overall, Cambodia's track record of consistent economic growth, coupled with its diversified economic base and proactive government policies, positions the country as a promising destination for investors seeking stability and long-term growth prospects in the region.
02STRATEGIC LOCATION AND REGIONAL CONNECTIVITY
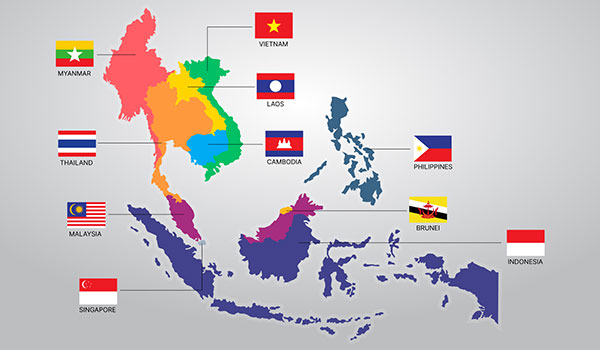
Cambodia's strategic location within Southeast Asia offers significant advantages for businesses looking to tap into regional markets. Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, the country serves as a gateway to the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) and the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS), comprising dynamic economies such as Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos.
The Kingdom's geographical proximity to key markets facilitates trade and investment flows, bolstered by extensive transport infrastructure developments. The expansion of road networks, including the Southern Economic Corridor and the Asian Highway Network, enhances connectivity within the region and facilitates the movement of goods and services.
Furthermore, Cambodia's membership in ASEAN provides access to a market of over 650 million people, offering significant opportunities for trade and investment. The ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and other regional agreements promote economic integration and facilitate cross-border business activities, creating a conducive environment for investors.
Moreover, Cambodia's participation in initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the Lancang-Mekong Cooperation (LMC) framework further strengthens its regional connectivity and enhances collaboration with neighboring countries. These strategic partnerships contribute to Cambodia's attractiveness as a hub for trade, investment, and economic cooperation in Southeast Asia.
03INVESTMENT-FRIENDLY POLICIES AND REFORMS

Cambodia has undertaken significant reforms to improve its investment climate and attract foreign capital. The government has implemented various initiatives to streamline bureaucratic processes, enhance transparency, and create a conducive environment for business growth.
The Law on Investment and Special Economic Zones (SEZs) provide investors with favorable incentives, including tax holidays, import duty exemptions, and simplified regulatory procedures. These measures aim to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and promote private sector-led economic development.
Additionally, Cambodia has prioritized key sectors for investment, including manufacturing, agribusiness, tourism, and infrastructure development. The establishment of sector-specific incentives and investment promotion agencies further supports targeted investment initiatives and encourages diversified economic growth.
Furthermore, the government's commitment to administrative efficiency and regulatory clarity is evident in initiatives such as the Single Portal for Business Registration and the National Single Window for Trade Facilitation. These platforms streamline business processes, reduce red tape, and improve the ease of doing business in Cambodia.
Overall, Cambodia's investment-friendly policies and proactive reforms demonstrate the government's commitment to fostering a conducive environment for sustainable economic growth and attracting foreign investment across various sectors.
04EXPANDING INFRASTRUCTURE AND DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS

Infrastructure development plays a crucial role in Cambodia's economic transformation and regional integration efforts. The government has prioritized investments in key infrastructure projects to enhance connectivity, facilitate trade, and support sustainable development across the country.
One notable project is the Phnom Penh-Sihanoukville Expressway, a major transportation corridor that links the capital city to the country's main seaport and industrial hub. This expressway reduces travel time and transportation costs, improving logistical efficiency and promoting economic activities along the route.
Additionally, Cambodia has made significant investments in port facilities, including the expansion of the Sihanoukville Autonomous Port, Cambodia's largest seaport. The port's modernization and capacity enhancements increase its competitiveness and position Cambodia as a regional logistics hub for maritime trade.
Furthermore, the government has prioritized investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including hydroelectric dams and solar power projects, to address growing energy demand and promote sustainable development. These initiatives contribute to Cambodia's transition towards cleaner and more resilient energy systems.
Moreover, urban development projects, such as the Phnom Penh City Center Master Plan and the development of satellite cities, aim to enhance livability, attract investment, and promote inclusive growth in urban areas.
Overall, Cambodia's ambitious infrastructure agenda and development projects create opportunities for investment across various sectors, stimulate economic growth, and enhance the country's competitiveness on the regional stage.
05EMERGING MARKET WITH COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES

Cambodia offers investors a unique blend of competitive advantages, including a young and skilled workforce, abundant natural resources, and a pro-business environment. The country's strategic location, coupled with its commitment to regional integration and economic diversification, positions Cambodia as a promising investment destination in Southeast Asia. With attractive valuations and untapped opportunities, Cambodia presents investors with the potential for high returns and long-term growth.